1. Client Access Server Architecture
You can already guess by
looking at the name of this Exchange Server role that it enables a
mailbox-enabled user to gain access to his or her mailbox using any of
the supported Client Access protocols: MAPI/RPC, POP3, IMAP4, HTTP, and Exchange ActiveSync.
1.1. Client Access Server Features
The Client Access
Server role has grown from previous versions. Microsoft introduced the
Client Access Server role in Exchange 2007 to replace the previous
situation where all mailbox clients either directly connected to the
mailbox server or via a proxy. The mailbox server did all of the logic
and rendering of data. A major architectural change came in Exchange
2007 and most of the Client Access protocols were consolidated on the
Client Access Server. This included Outlook Web Access (OWA), IMAP4,
POP3, Exchange Web Services, and Exchange ActiveSync. MAPI and WebDav clients still connected to the mailbox server directly.
Now in Exchange 2010, all business logic and data rendering takes place on the Client Access Server. Figure 1 illustrates all of the middle-tier services provided by the Exchange 2010 Client Access Server.
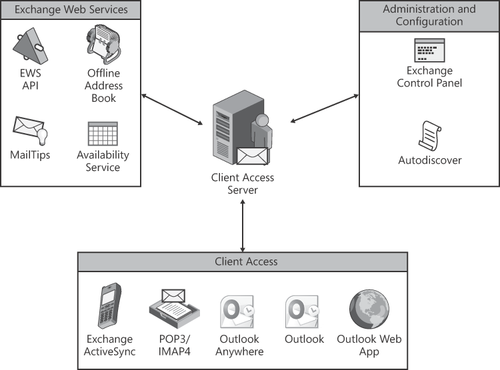
Along with this new architecture, the Client Access Server hosts a number of new features, as shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Client Access Server Features
| FEATURE NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|
| Outlook Web App | Outlook Web App enables Web-based clients to access their mailboxes. |
| RPC Client Access | RPC Client Access enables MAPI clients to access their mailboxes (such as Microsoft Outlook). |
| POP3/IMAP4 | POP3/IMAP4 enables clients such as Windows Live Mail to access their mailboxes. |
| Outlook Anywhere | Outlook Anywhere enables Microsoft Outlook 2003 or later clients to access their mailboxes using HTTP(S). |
| ActiveSync | ActiveSync
enables mobile phones running Exchange ActiveSync to synchronize
e-mail, contacts, calendar information, and tasks to the device. |
| Availability Service | The Availability Service provides clients with free/busy information. |
| Exchange Web Services (EWS) | Exchange Web Services provides an XML/SOAP interface for programmatic access to Exchange Server functionality. |
| MailTips | MailTips
analyzes message properties, including the recipients, and notifies
users of potential issues with the message before it is sent. |
| Exchange Control Panel (ECP) | The
Exchange Control Panel is a Web-based management interface that allows
administrators access to a set of administrative tasks. ECP also
provides user self-service capabilities. |
| AutoDiscover | AutoDiscover
enables Outlook 2007 and Outlook 2010 clients and Windows Mobile 6.1 or
later clients to auto-configure user profile settings. |
| Address Book Service | The Address Book Service replaces DSProxy for handling directory-related requests. |
2. Windows Services
Table 2 lists the Exchange services added to Windows when the Client Access Server role is installed.
Table 2. Exchange Services for the Client Access Server role
| SERVICE | DESCRIPTION | BEST PRACTICE INFORMATION |
|---|
| Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology | This
service reads information from all Active Directory partitions. The
data is cached and then used by Exchange 2010 servers to discover the
Active Directory site location of all Exchange services in the
organization. It is also responsible for updating the site attribute of
the Exchange server object in Active Directory. | Runs on all Exchange servers except Edge servers. Stopping this service is the quickest way to stop all Exchange services. |
| Microsoft Exchange Address Book | This service manages client address book connections and is dependent upon the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service. | This
service is required to register the Client Access server as the Name
Service Provider Interface (NSPI). This performs all directory
connections for clients. |
| Microsoft Exchange File Distribution | This
service is responsible for distributing the offline address book (OAB)
files, unified messaging prompts, and group metrics files. This service
is dependent on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology and Workstation services. | This
service is required to distribute the OAB files from the OAB generation
server to the Client Access server distribution points. |
| Microsoft Exchange Forms-Based Authentication Service | Provides forms-based authentication to Outlook Web App and the Exchange Control Panel. This service has no dependencies. | If this service is stopped, OWA and ECP users cannot authenticate. |
| Microsoft Exchange IMAP4 | Provides IMAP4 service to users. This service is dependent on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service. | This service is set to Manual by default. It must be set to Automatic if IMAP4 clients are connecting to this Client Access server. |
| Microsoft Exchange Mailbox Replication | This service processes mailbox move requests and is dependent on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service and the Net.Tcp port-sharing services. | This is an optional service. |
| Microsoft Exchange Monitoring | This service allows applications to call the Exchange diagnostic cmdlets. It has no dependencies. | This service should be started when you consider implementing monitoring tools such as System Center Operations Manager. |
| Microsoft Exchange POP3 | Provides POP3 service to users. This service is dependent on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service. | This service is set to Manual by default. It must be set to Automatic if POP3 clients are connecting to this Client Access server. |
| Microsoft Exchange Protected Service Host | Replaces services from the System Attendant functions in previous versions of Exchange. |
|
| Microsoft Exchange Service Host | Used to do GroupMetrics calculations for MailTips and ensures ValidPorts registry keys for Outlook Anywhere. |
|
| Microsoft Exchange RPC Client Access | This service manages client RPC connections and is dependent on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service. | This is a required service for MAPI clients to connect to their mailbox data. |